UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a newer standard that replaces the legacy BIOS. UEFI offers more features and benefits, such as faster boot times, better security, larger disk support, and a graphical user interface. Legacy BIOS is the old mode that uses a 16-bit code and a limited number of options. Basic UEFI and BIOS are two types of motherboard firmware used during startup to initialize the hardware and load the operating system. They also determine the device boot priority and allow users to customize hardware and software settings. However, UEFI is newer and offers more customization options and features. In this article, you will learn about UEFI and BIOS and how they differ. Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode is a feature that is related to the Thunderbolt technology and its integration with the computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). In the BIOS Assisted Mode, the BIOS pre-allocates resources including PCIe and Memory resources for use by the OS to handle adding and removing Thunderbolt devices. This ensures that devices that are added and removed do not negatively impact the system performance or user experience. By pre-allocating resources, Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode helps maintain system performance and stability. It ensures that the addition or removal of Thunderbolt devices does not cause any disruptions or slowdowns in the overall system operation. BIOS identifies, configures, tests, and connects computer hardware to the OS immediately after a computer is turned on. The combination of these steps is called the boot process. These tasks are each carried out by BIOS’ four main functions: Power-on self-test (POST). It provides a way to configure various hardware and system settings, such as boot order, date and time, device settings, and more. Yes, in certain cases, you may need to enable Thunderbolt in the BIOS before you can use Thunderbolt 3 hardware. Certain PC systems require that you manually enable Thunderbolt in the BIOS before any Thunderbolt 3 hardware can be used. The steps for entering the BIOS and changing this setting will vary depending on the computer/motherboard manufacturer and the BIOS version. We suggest referring to your computer or motherboard manual or reaching out to the manufacturer for guidance on adjusting BIOS settings. In certain situations, a BIOS update might be necessary to activate Thunderbolt capabilities before using Thunderbolt 3 hardware. You can usually find BIOS updates on the manufacturer’s website. However, if you’re unsure about updating your BIOS, it’s best to seek assistance from the computer or motherboard manufacturer. UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a newer standard that replaces the legacy BIOS. UEFI offers more features and benefits, such as faster boot times, better security, larger disk support, and a graphical user interface. Unlike traditional BIOS, UEFI offers numerous new features and advantages, aiming to eventually replace BIOS altogether. One notable feature is its ability to store initialization and startup information in a .efi file located on a specialized partition known as the EFI System Partition (ESP). This partition also houses boot loader programs for the installed operating system, enabling UEFI to directly boot the OS without undergoing the BIOS self-test process. This streamlined process contributes to faster boot times. Note: It’s worth noting that while some users may refer to UEFI boot as “BIOS,†most modern PCs today utilize UEFI firmware instead. To differentiate between UEFI and BIOS, some also use terms like “UEFI BIOS†for UEFI firmware and “Legacy BIOS†or “traditional BIOS†for BIOS. Changing Thunderbolt settings in the BIOS is a pretty straightforward process. here’s a general guide on how to do it: To unlock advanced settings in the BIOS, you need to keep in mind that the availability of advanced settings can vary depending on the manufacturer and model of your computer. Here are some general steps you can try: If this method does not work for you then I will suggest you try these possible ways as well; If none of the 3 ways, the Advanced settings are set to lock on your computer by your manufacturer and there is no way to unlock it. Note: It’s important to note that not all computers allow users to unlock advanced settings in the BIOS. Some manufacturers may restrict access to advanced settings to prevent users from making changes that could potentially damage the system. If you are unable to find the option to unlock advanced settings in your BIOS, likely, that your computer does not support it. BIOS and UEFI perform similar functions in a computer, although how they work behind the scenes is vastly different. While the newer standard is certainly the better option for modern devices, there’s no way to update your legacy motherboard to UEFI in case you’re wondering. The only way to switch to the newer technology would be a hardware upgrade. So are you running a new system with UEFI or a legacy motherboard with BIOS firmware? The main difference between UEFI and BIOS lies in their architecture and capabilities. While BIOS uses 16-bit mode and has a limited user interface, UEFI uses 32-bit or 64-bit mode and offers a more advanced graphical user interface. UEFI is a 32-bit or 64-bit program that is written in the C language. UEFI is not limited to real mode and provides more addressable address space. Legacy BIOS is a 16-bit program assembly language that can run only in 16-bit real mode and provides only 1 MB of addressable memory. Modifying BIOS settings can be risky, so always exercise caution. Incorrectly changing settings can cause the computer to not start, and some changes might damage the motherboard. It’s best to have some technical know-how before making BIOS changes. Here are some factors to consider when changing the BIOS mode: On the System Details page, select the Drive Encryption tab. Click More to see the firmware type. The firmware type will be either in BIOS or EFI (UEFI). Legacy BIOS mode is compatible with older hardware and operating systems that may not support UEFI. If you’re using older hardware or need to run older software that doesn’t support UEFI, legacy mode may be necessary. Legacy BIOS is generally considered more straightforward. Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification for a software program that connects a computer’s firmware to its operating system (OS). UEFI is expected to eventually replace basic input/output system (BIOS) but is compatible with it. UEFI mode is a newer and more advanced firmware interface that replaces the legacy BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). It allows for faster boot times, more secure boot processes, and support for larger disk sizes. Aluminium Window Screen,Aluminum Security Doors,Aluminum Security Screen Door,Aluminum Screen Wire Rolls SHENZHOU SHUANGYOU MESH CO.,LTD. , https://www.firstwiremesh.com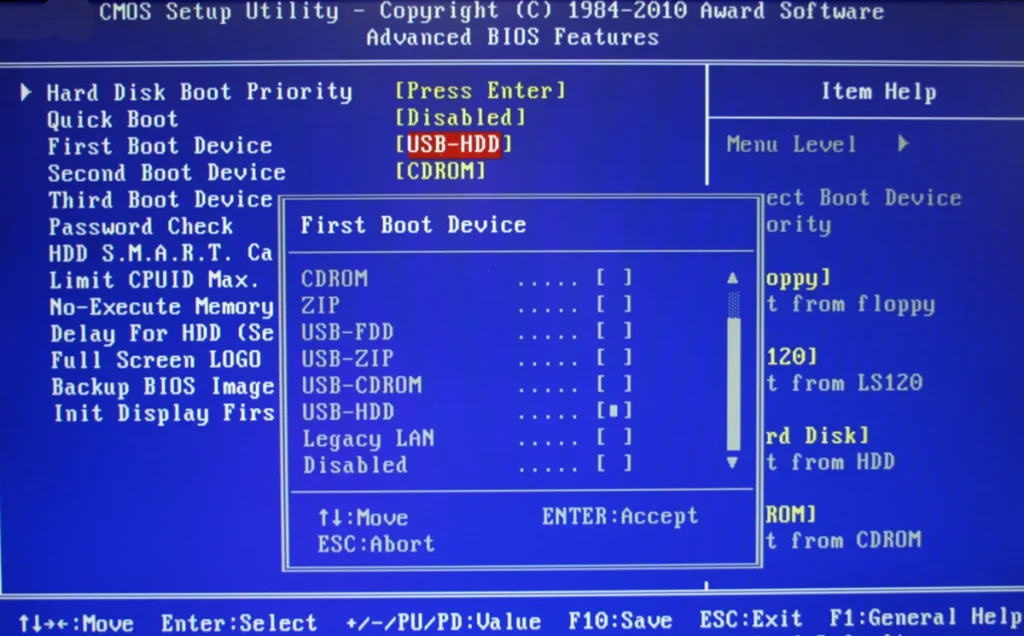
What is Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode?
When Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode is enabled, the BIOS reserves and allocates specific resources for Thunderbolt devices. This allocation helps prevent any negative impact on system performance or user experience when Thunderbolt devices are connected or disconnected.
Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode aims to provide a seamless user experience when working with Thunderbolt devices. It helps avoid potential issues that may arise from hot-plugging Thunderbolt devices, such as system crashes or performance degradation.What Does Bios Mode Do?
Here are some key functions and features of BIOS mode:Do I Need To Enable Thunderbolt In The Bios?
What is UEFI Boot Mode?
UEFI boot mode refers to the method by which a computer’s firmware, initializes hardware components and launches the operating system during startup. In UEFI boot mode, the system follows the UEFI specification to load and execute the boot loader, operating system kernel, and other necessary components directly from storage devices, such as hard disk drives or solid-state drives.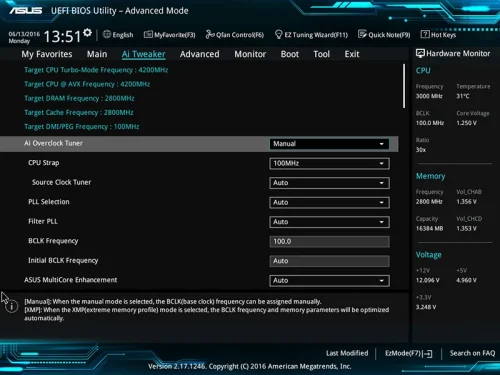
Compared to the traditional BIOS boot mode, UEFI boot mode offers several advantages, including faster startup times, support for larger storage devices and partitions, and more secure booting through features like Secure Boot. Additionally, UEFI boot mode enables advanced functionality, such as support for graphical interfaces during the boot process and the ability to run pre-boot applications and diagnosticsFunctions of UEFI Boot Mode:
What Is The Difference Between UEFI And Legacy Bios Mode?
BIOS
UEFI
Runs on Legacy Hardware
Runs on both legacy and newer hardware
Only supports DOS and Windows
Supports Windows, Linux, and Mac operating systems
Smaller file size and uses less memory
Larger file size and uses more memory but provides more functionality
Boots via traditional method from MBR
Boots via modern method from GPT partition
Limited to 2TB storage support
Supports storage devices larger than 2TB
Fixed 16-bit architecture
Moder 64-bit architecture that is upgradeable
Can only address lower memory
Supports High-resolution graphics and inputs
Firmware cannot be updated without a flash ROM chip
Firmware updates are easy and don’t require flash ROM chip replacement
Limitations in booting from external devices
Better support for booting from external devices like USB, SD cards, etc
How Do I Change Thunderbolt Settings In BIOS?
Restart your computer and enter the BIOS setup utility. This is typically done by pressing a specific key during the boot process, such as F2, Del, Esc, or F10. The correct key should be displayed on your screen during startup.
Once you’re in the BIOS setup utility, navigate through the menus using the arrow keys on your keyboard. Look for a section related to “Advanced†or “Peripheral Configuration†settings.
Within the advanced settings, there should be an option for Thunderbolt configuration. It may be labeled as “Thunderbolt Configuration,†“Thunderbolt Security,†or something similar.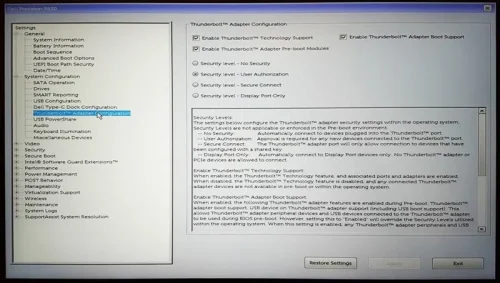
Enter the Thunderbolt configuration menu and you should see various options related to Thunderbolt ports, security features, and device settings. Depending on your needs, you can adjust settings such as Thunderbolt security levels, port configurations, and device enumeration.
After making your desired changes, navigate to the option to save your settings and exit the BIOS setup utility. This is typically done by selecting “Save Changes and Exit†or a similar option. Confirm your selection and your computer will reboot with the new Thunderbolt settings applied.How To Unlock Advanced Settings In BIOS?
What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
What is the difference between UEFI and Legacy BIOS?
Is It Safe To Change Bios Mode?
Ensure that your hardware and operating system support the desired BIOS mode. For example, if you want to switch from Legacy BIOS mode to UEFI mode, you need to verify that your hardware and operating system are compatible with UEFI.
Before making any changes to the BIOS mode, it is highly recommended to create a backup of your important data. This will help you recover in case any issues arise during the process.
Different computer manufacturers may have specific instructions or recommendations for changing the BIOS mode. It is advisable to consult the documentation or support resources provided by your computer manufacturer for accurate and detailed instructions.
In some cases, changing the BIOS mode may require updating the BIOS firmware. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when performing a BIOS update to avoid any potential risks.
Am I on UEFI or BIOS?
Why BIOS is better than UEFI?
Why is UEFI called BIOS?
Which is faster legacy or UEFI?
How to check BIOS?
Share This Artcle:
Aluminium Window Screen,Aluminum Security Doors,Aluminum Security Screen Door,Aluminum Screen Wire Rolls SHENZHOU SHUANGYOU MESH CO.,LTD. , https://www.firstwiremesh.com